- Java設計模式
- Java設計模式簡介
- 軟件設計模式
- GoF的23種設計模式的分類和功能
- UML中的類圖及類圖之間的關系
- Java代理模式
- Java靜態代理模式
- Java動態代理模式
- Java工廠模式
- Java工廠方法模式
- Java抽象工廠模式
- Java單例模式
- Java建造者模式
- Java原型模式
- Java適配器模式
- Java橋接模式
- Java過濾器模式
- Java裝飾器模式
- Java外觀模式
- Java享元模式
- Java責任鏈模式
- Java命令模式
- Java解釋器模式
- Java迭代器模式
- Java中介者模式
- Java備忘錄模式
- Java觀察者模式
- Java狀態模式
- Java空對象模式
- Java策略模式
- Java訪問者模式
- MVC設計模式
- 業務代表模式
- 數據訪問對象模式
- 前端控制器設計模式
- 攔截過濾器模式
- Java服務定位器模式
- Java傳輸對象模式
- 結構型模式
- 行為型模式
- Java創建型模式
- Java組合模式
- 組合實體模式
- Java模板模式
- Java模板方法模式
- UMLet的使用與類圖的設計
- 創建型模式應用實驗
- 結構型模式應用實驗
- 行為型模式應用實驗
Java享元模式
享元模式(Flyweight Pattern)主要用于減少創建對象的數量,以減少內存占用和提高性能。這種類型的設計模式屬于結構型模式,它提供了減少對象數量從而改善應用所需的對象結構的方式。
享元模式嘗試重用現有的同類對象,如果未找到匹配的對象,則創建新對象。我們將通過創建 5 個對象來畫出 20 個分布于不同位置的圓來演示這種模式。由于只有 5 種可用的顏色,所以 color 屬性被用來檢查現有的 Circle 對象。
介紹
意圖:運用共享技術有效地支持大量細粒度的對象。
主要解決:在有大量對象時,有可能會造成內存溢出,我們把其中共同的部分抽象出來,如果有相同的業務請求,直接返回在內存中已有的對象,避免重新創建。
何時使用:
⒈系統中有大量對象。
⒉這些對象消耗大量內存。
⒊這些對象的狀態大部分可以外部化。
⒋這些對象可以按照內蘊狀態分為很多組,當把外蘊對象從對象中剔除出來時,每一組對象都可以用一個對象來代替。
⒌系統不依賴于這些對象身份,這些對象是不可分辨的。
如何解決:用唯一標識碼判斷,如果在內存中有,則返回這個唯一標識碼所標識的對象。
關鍵代碼:用 HashMap 存儲這些對象。
應用實例:
⒈JAVA 中的 String,如果有則返回,如果沒有則創建一個字符串保存在字符串緩存池里面。
⒉數據庫的數據池。
優點:大大減少對象的創建,降低系統的內存,使效率提高。
缺點:提高了系統的復雜度,需要分離出外部狀態和內部狀態,而且外部狀態具有固有化的性質,不應該隨著內部狀態的變化而變化,否則會造成系統的混亂。
使用場景:
⒈系統有大量相似對象。
⒉需要緩沖池的場景。
注意事項:
⒈注意劃分外部狀態和內部狀態,否則可能會引起線程安全問題。
⒉這些類必須有一個工廠對象加以控制。
實現
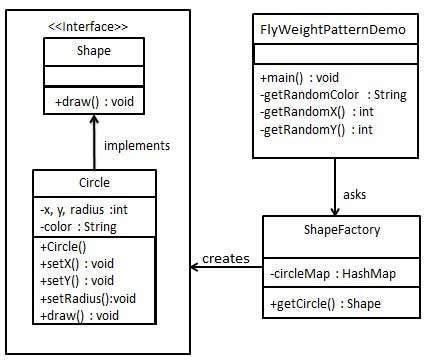
我們將創建一個 Shape 接口和實現了 Shape 接口的實體類 Circle。下一步是定義工廠類 ShapeFactory。
ShapeFactory 有一個 Circle 的 HashMap,其中鍵名為 Circle 對象的顏色。無論何時接收到請求,都會創建一個特定顏色的圓。ShapeFactory 檢查它的 HashMap 中的 circle 對象,如果找到 Circle 對象,則返回該對象,否則將創建一個存儲在 hashmap 中以備后續使用的新對象,并把該對象返回到客戶端。
FlyWeightPatternDemo,我們的演示類使用 ShapeFactory 來獲取 Shape 對象。它將向 ShapeFactory 傳遞信息(red / green / blue/ black / white),以便獲取它所需對象的顏色。
步驟 1
創建一個接口。
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}
步驟 2
創建實現接口的實體類。
public class Circle implements Shape {
private String color;
private int x;
private int y;
private int radius;
public Circle(String color){
this.color = color;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public void setRadius(int radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Circle: Draw() [Color : " + color
+", x : " + x +", y :" + y +", radius :" + radius);
}
}
步驟 3
創建一個工廠,生成基于給定信息的實體類的對象。
import java.util.HashMap;
public class ShapeFactory {
private static final HashMap circleMap = new HashMap<>();
public static Shape getCircle(String color) {
Circle circle = (Circle)circleMap.get(color);
if(circle == null) {
circle = new Circle(color);
circleMap.put(color, circle);
System.out.println("Creating circle of color : " + color);
}
return circle;
}
}
步驟 4
使用該工廠,通過傳遞顏色信息來獲取實體類的對象。
public class FlyweightPatternDemo {
private static final String colors[] =
{ "Red", "Green", "Blue", "White", "Black" };
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0; i < 20; ++i) {
Circle circle =
(Circle)ShapeFactory.getCircle(getRandomColor());
circle.setX(getRandomX());
circle.setY(getRandomY());
circle.setRadius(100);
circle.draw();
}
}
private static String getRandomColor() {
return colors[(int)(Math.random()*colors.length)];
}
private static int getRandomX() {
return (int)(Math.random()*100 );
}
private static int getRandomY() {
return (int)(Math.random()*100);
}
}
步驟 5
執行程序,輸出結果:
Creating circle of color : Black
Circle: Draw() [Color : Black, x : 36, y :71, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Green
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 27, y :27, radius :100
Creating circle of color : White
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 64, y :10, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Red
Circle: Draw() [Color : Red, x : 15, y :44, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 19, y :10, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 94, y :32, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 69, y :98, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Blue
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 13, y :4, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 21, y :21, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 55, y :86, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 90, y :70, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 78, y :3, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 64, y :89, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 3, y :91, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 62, y :82, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 97, y :61, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 86, y :12, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 38, y :93, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Red, x : 76, y :82, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 95, y :82, radius :100






