更新時間:2022-06-22 12:13:40 來源:動力節點 瀏覽1512次
這些運算符用于執行邏輯“與”、“或”和“非”運算,即類似于數字電子學中的與門和或門的功能。它們用于組合兩個或多個條件/約束或補充在特定考慮下對原始條件的評估。要記住的一件事是,如果第一個條件為假,則不會評估第二個條件,即它具有短路效應。廣泛用于測試做出決定的幾個條件。讓我們詳細了解每個邏輯運算符:
當考慮的兩個條件都滿足或為真時,此運算符返回真。如果兩者之一產生假,則運算符的結果為假。例如,當 cond1 和 cond2 都為真(即非零)時, cond1 && cond2 返回真。
句法:
條件1 && 條件2
插圖:
a = 10, b = 20, c = 20
條件1:a < b
條件2:b == c
如果(條件1 && 條件2)
d = a+b+c
// 因為兩個條件都為真
d = 50。
例子
// Java code to illustrate
// logical AND operator
import java.io.*;
class Logical {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// initializing variables
int a = 10, b = 20, c = 20, d = 0;
// Displaying a, b, c
System.out.println("Var1 = " + a);
System.out.println("Var2 = " + b);
System.out.println("Var3 = " + c);
// using logical AND to verify
// two constraints
if ((a < b) && (b == c)) {
d = a + b + c;
System.out.println("The sum is: " + d);
}
else
System.out.println("False conditions");
}
}
輸出:
變量 1 = 10
變量 2 = 20
變量 3 = 20
總和是:50
現在在下面的例子中,我們可以看到短路效應。這里當執行到 if 語句時,if 語句中的第一個條件為假,因此永遠不會檢查第二個條件。因此 ++b(b 的預增量)永遠不會發生并且 b 保持不變。
例子:
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
class shortCircuiting {
public static void main (String[] args) {
// initializing variables
int a=10,b=20,c=15;
// displaying b
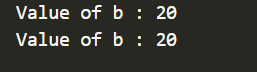
System.out.println("Value of b : "+b);
// Using logical AND
// Short-Circuiting effect as the first condition is false so the second condition is never reached and
// so ++b(pre increment) doesn't take place and value of b remains unchanged
if((a>c) && (++b>c)){
System.out.println("Inside if block");
}
// displaying b
System.out.println("Value of b : "+b);
}
}
輸出:
當考慮的兩個條件之一滿足或為真時,此運算符返回真。如果兩者中的任何一個都為真,則運算符的結果為真。要使結果為假,兩個約束都需要返回假。
句法:
條件1 || 條件2
例子:
a = 10, b = 20, c = 20
條件1:a < b
條件2:b > c
如果(條件1 || 條件2)
d = a+b+c
// 因為其中一個條件為真
d = 50。
// Java code to illustrate
// logical OR operator
import java.io.*;
class Logical {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// initializing variables
int a = 10, b = 1, c = 10, d = 30;
// Displaying a, b, c
System.out.println("Var1 = " + a);
System.out.println("Var2 = " + b);
System.out.println("Var3 = " + c);
System.out.println("Var4 = " + d);
// using logical OR to verify
// two constraints
if (a > b || c == d)
System.out.println("One or both"
+ " the conditions are true");
else
System.out.println("Both the"
+ " conditions are false");
}
}
輸出:
變量 1 = 10
變量 2 = 1
變量 3 = 10
變量 4 = 30
一個或兩個條件都為真
與前兩個不同,這是一個一元運算符,當考慮的條件不滿足或為假條件時返回真。基本上,如果條件為假,則操作返回真,當條件為真時,操作返回假。
句法:
!(健康)狀況)
例子:
a = 10, b = 20
!(a<b) // 返回 false
!(a>b) // 返回真
// Java code to illustrate
// logical NOT operator
import java.io.*;
class Logical {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// initializing variables
int a = 10, b = 1;
// Displaying a, b, c
System.out.println("Var1 = " + a);
System.out.println("Var2 = " + b);
// Using logical NOT operator
System.out.println("!(a < b) = " + !(a < b));
System.out.println("!(a > b) = " + !(a > b));
}
}
輸出:
變量 1 = 10
變量 2 = 1
!(a < b) = 真
!(a > b) = 假
以上就是關于“帶有示例的Java邏輯運算符介紹”,大家如果對此比較感興趣,想了解更多相關知識,可以關注一下動力節點的Java邏輯運算符,里面有更詳細的介紹等著大家去了解,希望對大家的學習能夠有所幫助。
 Java實驗班
Java實驗班
0基礎 0學費 15天面授
 Java就業班
Java就業班
有基礎 直達就業
 Java夜校直播班
Java夜校直播班
業余時間 高薪轉行
 Java在職加薪班
Java在職加薪班
工作1~3年,加薪神器
 Java架構師班
Java架構師班
工作3~5年,晉升架構
提交申請后,顧問老師會電話與您溝通安排學習