更新時間:2021-04-29 10:34:53 來源:動力節(jié)點 瀏覽1362次
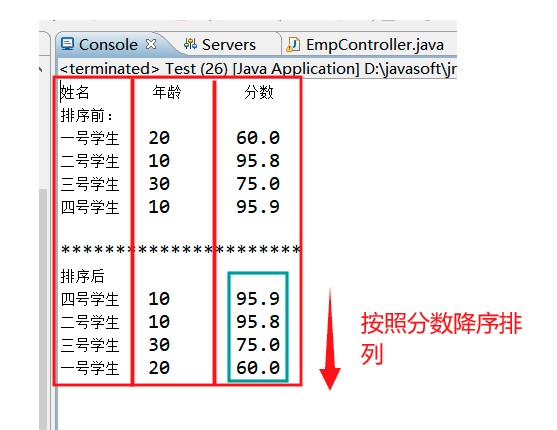
集合中存放了學(xué)生對象,按照學(xué)生分?jǐn)?shù)降序排序:
package cn.gf.exercise;
public class Stu {
private String stuno;
private String stuName;
private int age;
private double score;
//省略訪問器
}
package cn.gf.exercise;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//存放對象
Stu stu1 = new Stu();
stu1.setAge(20);
stu1.setScore(60);
stu1.setStuName("一號學(xué)生");
stu1.setStuno("001");
Stu stu2 = new Stu();
stu2.setAge(10);
stu2.setScore(95.8);
stu2.setStuName("二號學(xué)生");
stu2.setStuno("002");
Stu stu3 = new Stu();
stu3.setAge(30);
stu3.setScore(75);
stu3.setStuName("三號學(xué)生");
stu3.setStuno("003");
Stu stu4 = new Stu();
stu4.setAge(10);
stu4.setScore(95.9);
stu4.setStuName("四號學(xué)生");
stu4.setStuno("004");
ArrayList<Stu> stuList = new ArrayList<Stu>();
stuList.add(stu1);
stuList.add(stu2);
stuList.add(stu3);
stuList.add(stu4);
System.out.println("姓名 "+"\t"+" 年齡"+"\t"+" 分?jǐn)?shù)");
System.out.println("排序前:");
for(Stu s: stuList) {
System.out.println(s.getStuName()+"\t"+s.getAge()+"\t"+s.getScore());
}
System.out.println("");
//參數(shù)1:要排序的集合
//參數(shù)2:排序規(guī)則,排序接口的實現(xiàn)類,在實現(xiàn)類中重寫比較方法
Collections.sort(stuList,new Comparator<Stu>() {
@Override
public int compare(Stu o1, Stu o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//需要明確比較的內(nèi)容
/*按年齡排序的第一種方法
當(dāng)年齡相等的時候再按照成績排序
缺點:因為compare方法的返回值是int類型的,只適合整型的屬性排序,所以不夠靈活*/
// int i = o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
// if(i == 0) {
// return (int) (o1.getScore() - o2.getScore());
// }
// return i;
//返回0:相等 返回1:o1>o2 返回-1:o1<o2
//只按年齡排序第2中方法
// if(o1.getAge()>o2.getAge()){
// return 1;
// }else if(o1.getAge()<o2.getAge()){
// return -1;
// }else{
// return 0;
// }
//按成績
/*升序排序:大于配大值,小于配小值
* 降序排序:大于配小值,小于配大值
* (口訣:正序大配大,小配小;倒序相反)
*/
if(o1.getScore()>o2.getScore()) {
return -1;//大配小
}else if(o1.getScore()<o2.getScore()) {
return 1;//小配大,所以是降序排
}else {
return 0;
}
}
});
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("排序后");
for(Stu s: stuList){
System.out.println(s.getStuName()+"\t"+s.getAge()+"\t"+s.getScore());
}
}
}
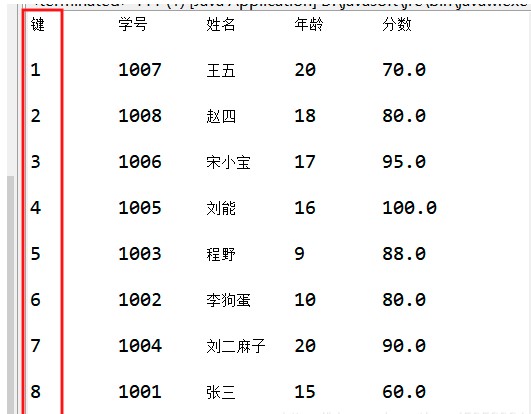
使用keySet()方法獲取HashMap集合的key,并存入Set集合中,所存放的Set集合已是升序排好的(原因是存的時候按照hash值大小來存的)(鍵是升序排好的,但并不代表鍵對應(yīng)的值是有序的):
package cn.gf.exercise;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class Map_Of_Sort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,Stu> map = new HashMap<String, Stu>();
Stu s1 = new Stu("1001", "張三", 15, 60);
Stu s2 = new Stu("1002", "李狗蛋", 10, 80);
Stu s3 = new Stu("1007", "王五", 20, 70);
Stu s4 = new Stu("1004", "劉二麻子", 20, 90);
Stu s5 = new Stu("1008", "趙四", 18, 80);
Stu s6 = new Stu("1005", "劉能", 16, 100);
Stu s7 = new Stu("1006", "宋小寶", 17, 95);
Stu s8 = new Stu("1003", "程野", 9, 88);
/*
因為put的時候會根據(jù)hash算法計算當(dāng)前key對應(yīng)的hash值,
所以插入進去的“鍵值對”會根據(jù)hash值(鍵)的大小在數(shù)組中排序, HashMap是數(shù)組+鏈表結(jié)構(gòu),
所以當(dāng)key為字符數(shù)字時,存的時候有序,取出來的key值也是有序的。
*/
map.put("8", s1);
map.put("7", s4);
map.put("1", s3);
map.put("6", s2);
map.put("5", s8);
map.put("4", s6);
map.put("3", s7);
map.put("2", s5);
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
Iterator<String> it = keys.iterator();
System.out.println("鍵"+"\t"+"學(xué)號"+"\t"+"姓名"+"\t"+"年齡"+"\t"+"分?jǐn)?shù)");
while(it.hasNext()) {
String next = it.next();
Stu s = map.get(next);
System.out.println();
System.out.println(next+"\t"+s.getStuno()+"\t"+s.getStuName()+"\t"+s.getAge()+"\t"+s.getScore());
}
}
}
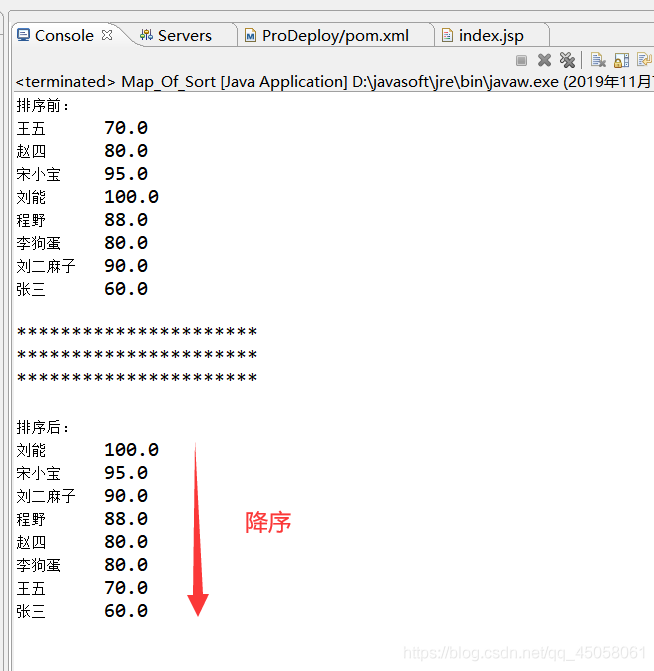
HashMap集合中存放了學(xué)生對象,按照學(xué)生的分?jǐn)?shù)降序排序:
思路:
1.通過map集合的entrySet()方法獲取每一對 “鍵----值” 對(此方法返回一個Set集合)
2.使用ArrayList集合的構(gòu)造方法,把Set集合轉(zhuǎn)化成list集合(因為Collections.sort()方法中只能傳入list集合)
3.調(diào)用Collections類的sort()方法,在sort()方法中自定義排序的規(guī)則
4.排序結(jié)束后map集合仍然是無序的,但是list集合是有序的(因為sort方法中傳入的參數(shù)是list)
package cn.gf.exercise;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
public class Map_Of_Sort {
@SuppressWarnings("unlikely-arg-type")
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,Stu> map = new HashMap<String, Stu>();
Stu s1 = new Stu("1001", "張三", 15, 60);
Stu s2 = new Stu("1002", "李狗蛋", 10, 80);
Stu s3 = new Stu("1007", "王五", 20, 70);
Stu s4 = new Stu("1004", "劉二麻子", 20, 90);
Stu s5 = new Stu("1008", "趙四", 18, 80);
Stu s6 = new Stu("1005", "劉能", 16, 100);
Stu s7 = new Stu("1006", "宋小寶", 17, 95);
Stu s8 = new Stu("1003", "程野", 9, 88);
map.put("8", s1);
map.put("7", s4);
map.put("1", s3);
map.put("6", s2);
map.put("5", s8);
map.put("4", s6);
map.put("3", s7);
map.put("2", s5);
//通過keySet()方法獲取所有的鍵,并存入Set集合中
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
//獲取keys集合的迭代器
Iterator<String> it = keys.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
/*
這樣獲取到的是null,會報錯
Stu stu2 = map.get(it);
*/
//通過迭代器的.next()方法來獲取key
String next = it.next();
//通過集合的.get(key)方法來獲取當(dāng)前鍵對應(yīng)的值
Stu stu = map.get(next);
//輸出未排序的集合
System.out.println(stu.getStuName()+"\t"+stu.getScore());
}
//通過map集合的entrySet()方法獲取 鍵---值對 (獲取map集合里的所有“映射”)
Set<Entry<String,Stu>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
/*編譯錯誤:
The method sort(List<T>, Comparator<? super T>)
in the type Collections is not applicable for
the arguments (Set<Map.Entry<String,Stu>>, new Comparator<Object>(){})
意思是:sort()方法只能傳入list集合,不能傳set集合
*/
//通過ArrayList集合的構(gòu)造方法,把set集合轉(zhuǎn)為list集合
ArrayList<Entry<String, Stu>> list = new ArrayList<>(entrySet);
/*
調(diào)用Collections.sort(List<T>, Comparator<? super T>)方法,自定義排序規(guī)則。
Parameters:
list: the list to be sorted.
c: the comparator to determine the order of the list. A null value indicates that the elements' naturalordering should be used.
*/
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Entry<String, Stu>>() {
@Override
public int compare(Entry<String, Stu> o1, Entry<String, Stu> o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(o1.getValue().getScore()>o2.getValue().getScore()) {
return -1;
}else if(o1.getValue().getScore()<o2.getValue().getScore()) {
return 1;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
});
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("**********************");
//因為Collection.sort()方法中傳入的是list集合,所以應(yīng)該遍歷list結(jié)合來判斷排序是否成功
for(Entry<String, Stu> e: list) {
System.out.println(e.getValue().getStuName()+"\t"+e.getValue().getScore());
}
}
}
以上就是動力節(jié)點小編介紹的"Java集合排序的方式"的內(nèi)容,希望對大家有幫助,如有疑問,請在線咨詢,有專業(yè)老師隨時為您服務(wù)。